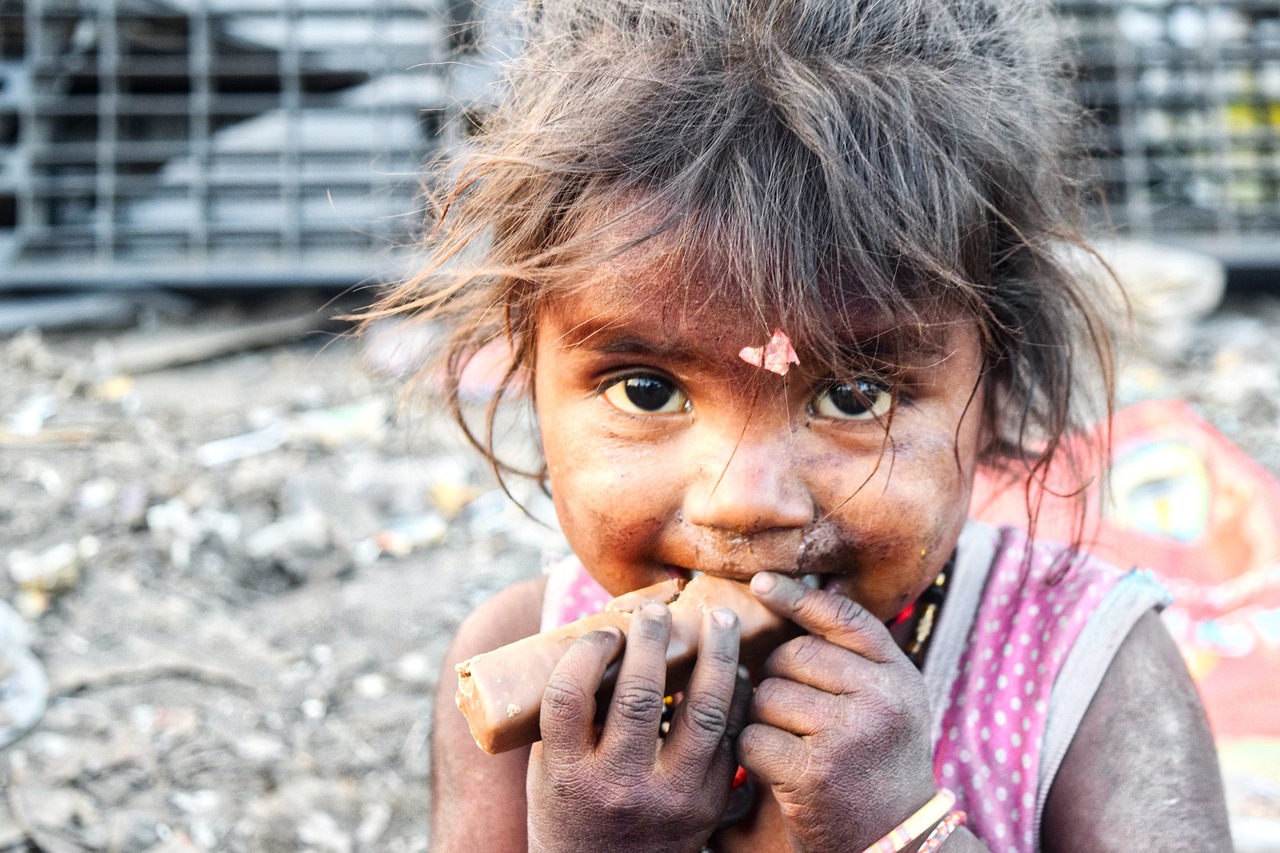
In a world where hunger continues to torment millions, corporate agriculture farming has emerged as a beacon of hope. The United Nations’ ambitious goal to eradicate hunger by 2030 has pushed the spotlight onto the critical role of corporate farming. In this article, we will explore the steps governments, international organizations, and individuals are taking to combat the food crisis and how corporate farming can contribute to this noble cause.
Understanding the Global Hunger Crisis
The 2023 Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) highlights a growing food crisis worldwide. It reveals that more than 250 million people are currently facing severe hunger, attributed in part to economic difficulties and the conflict in Ukraine. In 2022, a staggering 258 million individuals across 58 countries and regions experienced significant food insecurity, a notable increase from 2021 when 193 million people in 53 countries faced similar challenges.
Published by the Food Security Information Network (FSIN) and the Global Network against Food Crises (GNAFC), the GRFC 2023 offers a comprehensive overview of acute food insecurity in 2022, with a particular focus on countries identified by the report. This assessment is the result of collaboration among 16 partners who work collectively to analyze food insecurity situations, providing valuable evidence and guidance for both humanitarian and development efforts.
The Harsh Reality
The global hunger crisis remains an alarming concern as millions of people, including children; go to bed hungry every night. It is a grave injustice that amidst plenty, a significant portion of the world’s population still suffers from malnutrition and starvation.
UNO’s Ambitious Goal
The United Nations Organization (UNO) has set an brave target: to make the Earth hunger-free by 2030. This mission reflects the urgency of addressing this crisis and creating a world where no one has to tolerate the misery of hunger.
Russia-Ukraine War Mounts Global Hunger
The Russia-Ukraine war has had significant and far-reaching effects on food supplies worldwide, exacerbating the existing food crisis and highlighting the need for more sustainable and efficient food production methods, including corporate farming. Here is a detailed note on how this conflict has disrupted global food supplies and intensified the demand for corporate agriculture:
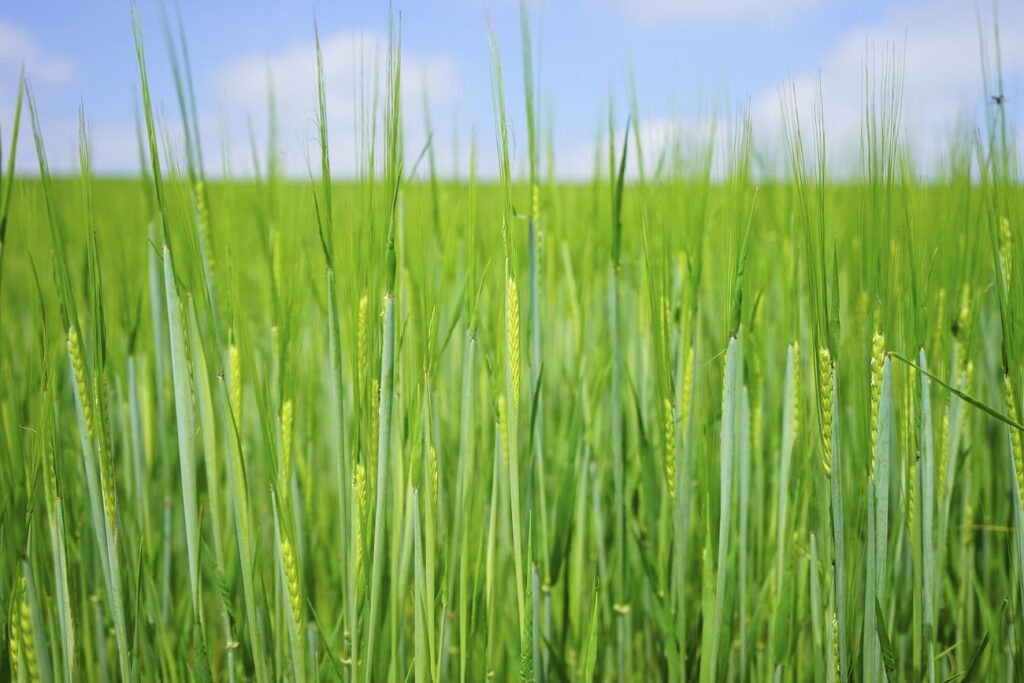
- Reduction in Agricultural Output: Ukraine and Russia are known as the “breadbasket of Europe” because they are major exporters of wheat and other grains. The war in the region disrupted agricultural operations, leading to a reduction in the planting and harvesting of crops. This reduction in agricultural output has contributed to a global decrease in the availability of staple foods, including wheat, corn, and barley.
- Export Restrictions: Both Ukraine and Russia imposed export restrictions on agricultural products due to the conflict. These restrictions limit the flow of grains and other food items to international markets, driving up prices and causing concerns about food shortages in many countries that rely on these exports.
- Global Price Increases: The reduced supply of grains from Ukraine and Russia has led to a surge in global commodity prices. This price increase has a cascading effect on food prices worldwide, making essential food items less affordable for vulnerable populations and exacerbating food insecurity.
- Uncertainty in Trade Routes: The conflict has disrupted trade routes and transportation infrastructure, making it challenging to move food from production areas to distribution centers and markets. This disruption has added complexity to the already intricate global food supply chain.
- Increased Vulnerability: The food crisis caused by the Russia-Ukraine war has made many regions more vulnerable to hunger and malnutrition. In particular, countries that heavily rely on imported grains from the affected region face greater food insecurity, potentially leading to humanitarian crises.
- Corporate Farming as a Solution: Corporate agriculture farming, characterized by large-scale, technologically advanced operations, has gained prominence as a potential solution to these food supply disruptions. These farms can produce significant quantities of food efficiently and reliably. They have the capacity to bridge the gap created by reduced agricultural output in regions affected by conflict.
- Technology and Efficiency: Corporate farms often invest in advanced technology and sustainable practices, leading to increased crop yields and reduced wastage. These innovations are crucial in ensuring a stable and consistent food supply.
- Economic Growth: Corporate farming operations create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth, especially in rural areas. This economic empowerment can contribute to poverty reduction and improved living standards, indirectly addressing food insecurity.
- Balancing Corporate Farming: While corporate farming offers benefits, it is essential to strike a balance. There is a need for policies that ensure that small-scale farmers are not marginalized and that sustainable practices are upheld to protect the environment and traditional farming methods.
In conclusion, the Russia-Ukraine war has disrupted global food supplies, leading to increased food prices and vulnerability to hunger in many regions. Corporate agriculture farming is being considered as a viable solution to bridge the food supply gap created by this conflict. However, responsible decision-making, collaboration among stakeholders, and a commitment to sustainable agriculture are crucial to ensure that the benefits of corporate farming are harnessed while mitigating its potential downsides
Steps Taken by Governments
Agricultural Reforms
Many governments worldwide are implementing agricultural reforms to boost food production. These reforms encompass the modernization of farming techniques, the promotion of sustainable practices, and the allocation of resources for research and development.
Subsidies and Support
Governments are also providing subsidies and financial support to small-scale farmers, enabling them to improve their productivity and livelihoods.
Efforts by International Organizations
Humanitarian Aid
International organizations such as the World Food Programme (WFP) play a crucial role in providing humanitarian aid to famine-stricken regions. They ensure that food reaches those who need it most, even in conflict zones and remote areas.
Advocating Sustainable Agriculture
These organizations advocate for sustainable farming practices to ensure long-term food security while preserving the environment.
Roll of NGOs
Two prominent nonprofit organizations, Welthungerhilfe in Germany and Concern Worldwide globally, share a common goal of combating hunger and extreme poverty. Welthungerhilfe aims to eliminate hunger entirely by 2030 and provides assistance for both growth and emergencies. Concern Worldwide focuses on impoverished regions with the aim of eradicating extreme poverty worldwide.
However, despite these efforts, the global hunger situation remains concerning, as highlighted in the 2022 Global Hunger Index (GHI) report. Various concurrent challenges in the food supply chain have exposed vulnerabilities, making people worldwide susceptible to hunger. Progress toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals of eradicating hunger is regressing, leading to worsening conditions in many areas.
Africa faces a significant risk of experiencing a severe food shortage crisis, and the current available assistance may fall short of meeting the growing demand. This crisis reflects a potential failure of the global food system and a disregard for people’s fundamental right to food.
Urgent action is needed to address the root causes of hunger and malnutrition. It is crucial to strengthen global systems, promote fairness, and ensure long-term sustainability to effectively eliminate hunger for good.
Individual Contributions
Food Donations
Individuals can contribute by donating food to local food banks and participating in initiatives like food drives to support those in need.
Conscious Consumption
Being careful consumers, individuals can reduce food waste and make sustainable choices in their diets, ultimately reducing the overall demand for food.
The Role of Corporate Agriculture Farming
Corporate agriculture farming can be a game-changer in the fight against global hunger. Here’s how:
Scale and Efficiency
Large-scale corporate farms can produce vast quantities of food efficiently, helping to meet the growing demand.
Innovation and Technology
Corporate farming invests in cutting-edge technology, which enhances crop yields and reduces wastage.
Sustainable Practices
Many corporate farms are adopting sustainable and eco-friendly farming practices, minimizing the negative impact on the environment.
Economic Empowerment
Corporate farming creates jobs and stimulates economic growth in rural areas, contributing to poverty reduction.
Drawbacks of Corporate Farming
Corporate agriculture farming offers both benefits and drawbacks that require careful consideration, particularly in low-production nations like Pakistan. While advantages like increased productivity, access to technology, infrastructure development, and job creation are enticing, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential disadvantages such as environmental concerns, the loss of traditional practices, and social inequalities.
For countries with limited agricultural output, corporate agriculture presents an opportunity to modernize their agricultural sector and address food security issues. However, striking a balance between large-scale farming and sustainable practices that respect local traditions and protect the environment is essential.
Countries contemplating the adoption of corporate agriculture should establish policies that prioritize the well-being of small-scale farmers, promote sustainable farming methods, and facilitate technology transfer and knowledge sharing. This approach allows them to harness the benefits of corporate agriculture while mitigating its potential downsides.
Conclusion
The global hunger crisis is a multifaceted challenge, and it requires a collective effort from governments, international organizations, individuals, and corporate agriculture farming. The UNO’s goal of achieving a hunger-free world by 2030 is within reach if we allocate resources with equitable measures and commit to sustainable, responsible farming practices. Together, we can make hunger a thing of the past.
FAQs
1. What is corporate agriculture farming?
Corporate agriculture farming refers to large-scale farming operations run by corporations. These farms produce food on a massive scale, often using advanced technology and sustainable practices.
2. How can individuals contribute to combating global hunger?
Individuals can contribute by donating food, reducing food waste, and making sustainable choices in their diets.
3. What are the benefits of corporate farming?
Corporate farming can increase food production, promote economic growth, and invest in technology for efficient farming.
4. What are the drawbacks of corporate farming?
Drawbacks include environmental concerns, the potential loss of traditional practices, and social inequalities in areas where corporate farming operates.
5. What is the United Nations’ goal regarding global hunger?
The UN aims to eradicate hunger worldwide by 2030, reflecting a commitment to making the world hunger-free.










One Comment