In today’s global economy, developing countries face a significant challenge when it comes to competing with developed nations. Developing countries often lack the resources and infrastructure required to keep up with the developed world’s rapid pace of technological advancement. However, with the right strategies in place, developing countries can compete on a more level playing field. In this article, we will explore some future strategies that poor and developing countries can adopt to compete with the developed world, including which fields they should focus on first, and how to implement those policies.
The development of a country is a complex issue that encompasses economic, political, and social factors. Economic development is often a key focus for developing countries, as it involves increasing productivity, creating jobs, and improving living standards. However, political and social factors can also play a significant role in development, such as the stability of the government, access to education and healthcare, and the promotion of human rights. Therefore, the development of a country is not limited to a single issue but instead requires a holistic approach that takes into account various economic, political, and social factors.
Introduction
The rapid pace of technological advancement and globalization has made it increasingly challenging for developing countries to compete with the developed world. Poor and developing countries face multiple challenges, from limited access to education and healthcare to inadequate infrastructure and lack of investment. However, developing countries can adopt future strategies to overcome these challenges and compete on a more level playing field.
Overview of the Challenges Facing Developing Countries
Developing countries face hundreds of thousands of challenges that make it difficult for them to compete with the developed world. These challenges include:
- Limited access to education and training
- Inadequate infrastructure and lack of investment
- Insufficient healthcare and social welfare systems
- Poor governance and corruption
- High levels of poverty and income inequality
- Limited access to technology and information
Importance of Future Strategies for Developing Countries
Future strategies are critical for developing countries because they provide a roadmap for how to overcome the challenges they face. By implementing future strategies, developing countries can create a more conducive environment for economic growth, innovation, and investment. They can also attract foreign investment, create jobs, and raise living standards for their citizens.
Identifying the Fields that Developing Countries Should Focus on
Developing countries should focus on several key fields to compete with the developed world. These fields include:
- Education and training
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Infrastructure development and investment
- Technological advancements
- Space Technology
- Sustainable policies
- Collaborating with Developed Countries
Investment in Education and Training
Investment in education and training is critical for developing countries to create a skilled workforce that can compete with the developed world. Developing countries should invest in education and training programs that are tailored to their specific needs and align with their economic development goals. By prioritizing access to education, focusing on vocational training and higher education, partnering with international organizations, aligning education and training with economic development goals, and emphasizing lifelong learning, developing countries can create a workforce that is well-equipped to compete with the developed world.
- Prioritize access to education: Developing countries should prioritize ensuring that all citizens have access to basic education, including primary and secondary schooling.
- Focus on vocational training: Vocational training programs can provide practical skills and knowledge that are directly applicable to the job market, helping individuals to find meaningful employment.
- Invest in higher education: Developing countries should also invest in higher education, such as universities and technical schools, to provide advanced training for professionals in fields such as medicine, engineering, and business.
- Partner with international organizations: Developing countries can partner with international organizations to access funding and expertise for education and training programs.
- Align education and training with economic development goals: Education and training programs should be designed to align with the economic development goals of the country, with a focus on developing skills and knowledge that are in high demand in the job market.
- Emphasize lifelong learning: Developing countries should emphasize the importance of ongoing education and training throughout an individual’s career, to adapt to changing job market demands and new technological advancements.
Encouraging Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Developing countries should encourage entrepreneurship and innovation by creating a supportive environment for startups and small businesses. This can be done by providing access to capital, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and creating tax incentives.
- Create a supportive environment for startups and small businesses.
- Provide access to capital to help fund new ventures.
- Reduce bureaucratic hurdles to make it easier for entrepreneurs to start businesses.
- Create tax incentives to encourage entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Develop partnerships between the private and public sectors to support innovation and growth.
- Foster a culture of risk-taking and experimentation to encourage entrepreneurial thinking.
- Promote collaboration between entrepreneurs and established businesses to drive innovation.
- Invest in research and development to create new products and services that can compete in the global market.
- Encourage the development of local industries to foster innovation and growth.
- Provide education and training programs to help entrepreneurs and innovators develop the skills they need to succeed.
Adopting Technological Advancements
Developing countries should adopt technological advancements to increase their productivity and competitiveness. This can be achieved by investing in research and development, creating partnerships with technology companies, and promoting technology transfer. There are several technological advancements that developing countries can prefer to promote economic growth and development. Here are some examples:
- Mobile Technology: Developing countries can leverage mobile technology to increase access to information, promote financial inclusion, and provide better healthcare services.
- Renewable Energy: Investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower can help developing countries reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources and promote environmental sustainability.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing can help developing countries improve their IT infrastructure and reduce the cost of data storage and management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can help developing countries automate processes, increase efficiency, and improve decision-making in various sectors, such as healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT can help developing countries improve resource management, reduce waste, and increase productivity in various sectors, such as agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can help developing countries promote financial inclusion, improve supply chain management, and reduce corruption.
These are just a few examples of the areas where technological advancement is most needed in the 21st century. As technology continues to evolve, it’s essential to prioritize innovation and invest in research and development to address the world’s most pressing challenges. It’s important to note that the specific technologies chosen will depend on the distinctive needs and circumstances of each country.
Space Technology
Space technology is a crucial technological advancement that has the potential to benefit humanity in many ways. Here are some examples:
- Satellite Communication: Satellites in orbit enable global communication and provide vital services, such as weather forecasting, GPS, and disaster management.
- Space Exploration: Space exploration has led to important scientific discoveries and technological innovations, such as materials science, robotics, and life support systems, which have practical applications on Earth.
- Earth Observation: Satellites equipped with sensors and cameras can provide data on climate change, deforestation, urbanization, and natural disasters, which can inform decision-making in various sectors, such as agriculture, forestry, and urban planning.
- Space Tourism: While still in its infancy, space tourism has the potential to promote education, inspire innovation, and generate revenue for the space industry.
- Space Mining: The exploration and exploitation of space resources, such as water, minerals, and metals, could provide new opportunities for economic growth and development.
These are just a few examples of the potential benefits of space technology. As space technology continues to evolve, it’s important to consider the ethical and environmental implications of space exploration and ensure that it benefits all of humanity.
Infrastructure Development and Investment
Developing countries should prioritize infrastructure development and investment to support economic growth. This can include investing in transportation, energy, water, and telecommunications infrastructure.
- Develop and maintain transportation infrastructure, including roads, bridges, railways, and airports, to improve connectivity and facilitate trade.
- Invest in energy infrastructure, such as power plants and distribution networks, to provide reliable and affordable energy to businesses and households.
- Improve access to clean water and sanitation by investing in water treatment facilities and distribution systems.
- Expand and modernize telecommunications infrastructure, including internet and mobile networks, to promote connectivity and digital inclusion.
- Invest in renewable energy infrastructure to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the negative environmental impacts of economic growth.
- Prioritize infrastructure development in underdeveloped and rural areas to promote more equitable economic growth.
- Develop public-private partnerships to finance and implement large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Implement policies and regulations that encourage private sector investment in infrastructure development.
- Prioritize maintenance and repair of existing infrastructure to ensure long-term sustainability and avoid costly replacements.
- Invest in human capital development to build a skilled workforce capable of designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure.
Collaborating with Developed Countries and International Organizations
Developing countries should collaborate with developed countries and international organizations to promote economic growth and development. This can involve sharing best practices, promoting trade and investment, and engaging in research and development partnerships.
- Share best practices: Developing countries can learn from the successes and failures of developed countries by sharing best practices. This can include sharing knowledge on policy implementation, infrastructure development, and technological advancements.
- Promote trade and investment: Developing countries can attract foreign investment by promoting their trade policies and incentives. This can include offering tax breaks, free trade zones, and streamlined regulations for foreign investors.
- Engage in research and development partnerships: Developing countries can collaborate with developed countries and international organizations on research and development projects. This can include partnerships on technological advancements, environmental sustainability, and health initiatives.
- Access to funding: Developing countries can leverage partnerships with developed countries and international organizations to access funding for economic development initiatives. This can include grants, loans, and other financial assistance.
- Encourage cultural exchange: Developing countries can promote cultural exchange programs with developed countries to foster a better understanding of each other’s cultures and promote economic ties. This can include student exchange programs, cultural festivals, and business delegations.
Implementation of Sustainable Policies
Developing countries should implement sustainable policies to promote environmental sustainability and mitigate the negative effects of economic development. This can include investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable agriculture practices, and protecting natural resources.
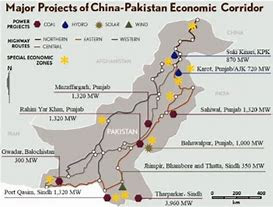
Lesson to Learn for Pakistan
There are several steps that Pakistan can take to develop like a developed world of the 21st century:
- Prioritize Education: Pakistan needs to invest more in education, especially in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields, to create a highly skilled workforce that can drive innovation and economic growth.
- Promote Women’s Empowerment: Pakistan needs to promote women’s education and employment opportunities, as studies show that gender equality is positively associated with economic development.
- Educate the Public: Raise public awareness about the importance of sustainable development and promote environmentally friendly behaviour through education campaigns.
- Support Sustainable Agriculture: Promote sustainable agriculture practices such as crop rotation, organic farming, and efficient irrigation techniques to reduce soil degradation and promote food security.
- Protect Natural Resources: Protect forests, wetlands, and other natural resources from overexploitation, deforestation, and pollution.
- Reduce Waste: Implement recycling programs and promote waste reduction initiatives to reduce the amount of waste produced and minimize the negative impact on the environment.
- Encourage Green Business Practices: Encourage businesses to adopt environmentally sustainable practices, such as reducing energy consumption, using eco-friendly products, and implementing waste reduction strategies.
- Focus on Renewable Energy: Pakistan should prioritize the development of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce carbon emissions, improve access to electricity, and promote sustainable development.
- Encourage Entrepreneurship: Pakistan needs to create a supportive environment for entrepreneurs and startups, with access to funding, mentorship, and regulatory frameworks that promote innovation and business growth.
- Improve Infrastructure: Pakistan should invest in improving its infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and water management systems, to facilitate trade and economic development.
- Improve Public Transportation: Invest in public transportation systems to reduce dependence on private vehicles, which contribute to air pollution and traffic congestion.
- Create Incentives: Provide financial incentives, such as tax breaks or subsidies, for businesses and individuals who adopt environmentally sustainable practices.
- Leverage Technology: Pakistan should leverage technology to address its social, economic, and environmental challenges, such as healthcare, agriculture, and disaster management.
- Address Political Instability: Pakistan must address political instability and create a conducive environment for business and investment, with strong institutions and a transparent regulatory framework.
- Collaborate with Other Countries: Collaborate with other countries to share best practices and promote international cooperation on environmental sustainability issues.
These are just a few steps Pakistan can take to develop like a world of the 21st century. By prioritizing education, renewable energy, entrepreneurship, infrastructure, women’s empowerment, technology, and political stability, Pakistan can build a strong foundation for sustainable economic growth and development. Japan is a prime example of a country that was able to rebuild and thrive after the devastation of nuclear war. Despite the challenges they faced, the Japanese people demonstrated resilience and determination in their efforts to rebuild their country. Their success is a testament to the power of human perseverance and the importance of prioritizing sustainable development. By studying the example of Japan, developing countries can learn valuable lessons about how to overcome adversity and build a better future for their citizens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing countries face many challenges in competing with the developed world in the 21st century. However, by prioritizing technological advancement, investing in education and skills development, and implementing sustainable policies, these countries can make significant progress towards achieving economic, social, and environmental sustainability. It is important for governments to prioritize the needs of their citizens and to work towards creating a sustainable future for all. By adopting a holistic approach that takes into account economic, social, and environmental factors, developing countries can build a better future for themselves and for the world as a whole.
FAQs
What is the importance of future strategies for developing countries?
- Future strategies provide a roadmap for how to overcome the challenges facing developing countries and create an environment that is conducive to economic growth and development.
What fields should developing countries focus on to compete with the developed world?
- Developing countries should focus on education and training, entrepreneurship and innovation, technological advancements, infrastructure development and investment, sustainable policies, and collaborating with developed countries and international organizations.
How can developing countries encourage entrepreneurship and innovation?
- Developing countries can encourage entrepreneurship and innovation by creating a supportive environment for startups and small businesses, providing access to capital, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and creating tax incentives.
What is the role of collaboration with developed countries and international organizations in promoting economic growth and development?
- Collaboration with developed countries and international organizations can involve sharing best practices, promoting trade and investment, and engaging in research and development partnerships, which can help promote economic growth and development.
What is the role of sustainable policies in promoting economic growth and development in developing countries?
- Sustainable policies can help promote environmental sustainability and mitigate the negative effects of economic development, which can help promote long-term economic growth and development in developing countries.